前言
- Vue CLI 是一个基于
Vue.js 进行快速开发的完整系统,其通过
@vue/cli
实现交互式的项目脚手架,并致力于将 Vue
生态中的工具基础标准化。它确保了各种构建工具能够基于智能的默认配置即可平稳衔接,这样可以专注在撰写应用上,而不必花好几天去纠结配置的问题,与此同时,它也为每个工具提供了调整配置的灵活性。
- Vuex
是一个专门为 Vue.js
应用程序开发的一种状态(数据)管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用程序的所有组件的状态(数据),并以相应的规则保证状态以可预测的方式变化。
1
| npm install vuex@3 --save
|
- vue-router是Vue.js官方的路由插件,它和vue.js是深度集成的,适合用于构建单页面应用。vue的单页面应用是基于路由和组件的,路由用于设定访问路径,并将路径和组件映射起来。传统的页面应用,是用一些超链接来实现页面切换和跳转的。在vue-router单页面应用中,则是路径之间的切换,也就是组件的切换。
1
| npm install vue-router@3
|
在本文的最后,补充了Vue
UI组件库Element UI的相关内容。
一、vue-cli
1.1 脚手架文件结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| ├── node_modules
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico: 页签图标
│ └── index.html: 主页面
├── src
│ ├── assets: 存放静态资源
│ │ └── logo.png
│ │── component: 存放组件
│ │ └── HelloWorld.vue
│ │── App.vue: 汇总所有组件
│ │── main.js: 入口文件
├── .gitignore: git版本管制忽略的配置
├── babel.config.js: babel的配置文件
├── package.json: 应用包配置文件
├── README.md: 应用描述文件
├── package-lock.json:包版本控制文件
|
1.1.1 main.js
- 这里引入的vue是
node_modules下的vue.runtime.xxx.js,是运行版的Vue,只包含核心功能,没有模板解析器
- 因为
vue.runtime.xxx.js没有模板解析器,所以不能使用template这个配置项,需要使用render函数接收到的createElement函数去指定具体内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
|
1.1.2 组件名.vue
语法同非单文件组件一样,只不过拆成了template、script、style三个部分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <template>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: '组件名'
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|
1.2 ref属性
- 被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(
id的替代者)
- 应用在html标签上获取的是真实DOM元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<h1 ref="xxx">.....</h1>
<School ref="xxx"></School>
this.$refs.xxx
|
1.3 $nextTick
- 当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新DOM进行某些操作时,使用nextTick。
- 作用:在下一次 DOM 更新结束后执行其指定的回调
- 语法:
this.$nextTick(回调函数)
1
2
3
4
|
this.$nextTick(function(){
this.$refs.inputTitle.focus()
})
|
1.4 scoped
让样式在局部组件生效,防止冲突
1.5 props配置项
- 功能:让组件接收外部传过来的数据
- 传递数据:
<Demo name="xxx"/>
- 接收数据:
- 第一种方式(只接收):
props:['name']
- 第二种方式(限制类型):
props:{name:String}
- 第三种方式(限制类型、限制必要性、指定默认值)
app.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <template>
<div>
<Student name="李四" sex="女" :age="18"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student'
export default {
name:'App',
components:{Student}
}
</script>
|
Student.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
props:['name','age','sex']
props:{
name:String,
age:Number,
sex:String
}
props:{
name:{
type:String,
required:true,
},
age:{
type:Number,
default:99
},
sex:{
type:String,
required:true
}
}
|
1.6 webStorage
- 存储内容大小一般支持5MB左右(不同浏览器可能还不一样)
- 浏览器端通过
Window.sessionStorage 和
Window.localStorage 属性来实现本地存储机制
sessionStorage存储的内容会随着浏览器窗口关闭而消失localStorage存储的内容需要手动清除才会消失
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
localStorage.setItem('key', 'value')
localStorage.getItem('key')
localStorage.removeItem('key')
localStorage.clear()
sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value')
sessionStorage.getItem('key')
sessionStorage.removeItem('key')
sessionStorage.clear()
|
1.7 子组件向父组件通信
1.7.1 父组件绑定自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<Demo @事件名="test"/>
<Demo v-on:事件名="test"/>
<Demo ref="demo"/>
......
mounted(){
this.$refs.demo.$on('事件名',this.test)
this.$refs.demo.$once('事件名',()=>{
...
})
}
|
1.7.2 子组件触发自定义事件
1
| this.$emit('事件名', '传递数据')
|
1.7.3 子组件解绑自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
this.$off('事件名1')
this.$off(['事件名1','事件名2'])
this.$off()
|
1.7.4 给子组件绑定原生DOM事件
组件上也可以绑定原生DOM事件,需要使用native修饰符
1
2
3
4
5
| <Student @click.native="show"/>
...
show(){
alert(123)
}
|
1.8 全局事件总线
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信
1.8.1 安装全局事件总线
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| new Vue({
...
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
},
...
})
|
1.8.2 使用全局事件总线
接受数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| methods(){
demo(data){...}
}
...
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on('事件名',this.方法名)
}
|
1
| this.$bus.$emit('事件名',数据)
|
1.8.3 解绑所用事件
1
2
3
| beforeDestroy() {
this.$bus.$off('事件名')
}
|
1.9 插槽
让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入html结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于
父组件 ===> 子组件
1.9.1 默认插槽
组件中的内容会填充到插槽slot内,下例父组件的div会替换子组件的slot
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 父组件中:
<Category>
<div>html结构1</div>
</Category>
子组件中:
<template>
<div>
<slot>插槽默认内容</slot>
</div>
</template>
|
1.9.2 具名插槽
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 父组件中:
<Category>
<div v-slot:center>html结构</div>
</Category>
子组件中:
<template>
<div>
<slot name="center">插槽默认内容</slot>
</div>
</template>
|
1.9.3 作用域插槽
数据在子组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要父组件的使用者来决定。(下例中foods数据在Category组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App组件决定)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| 父组件中:
<Category title="美食">
<template v-slot:food="slots">
<h4 v-for="(f, index) in slots.foods" :key="index">{{f}}</h4>
</template>
</Category>
子组件中:
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{title}}分类</h3>
<slot name="food" :foods="foods"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Category',
props:['title'],
data(){
return {
foods:['火锅', '烧烤', '小龙虾', '牛排'],
}
}
}
</script>
|
1.10 脚手架配置代理
1.10.1 方法一
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置
1
2
3
| devServer:{
proxy:"http://localhost:5000"
}
|
- 优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端(8080)即可
- 缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理
- 工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器
1.10.2 方法二
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| module.exports = {
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/api1': {
target: 'http://localhost:5000',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {'^/api1': ''}
},
'/api2': {
target: 'http://localhost:5001',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {'^/api2': ''}
}
}
}
|
- 优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理
- 缺点:配置略微繁琐,请求资源时必须加前缀
二、VueX
在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对Vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
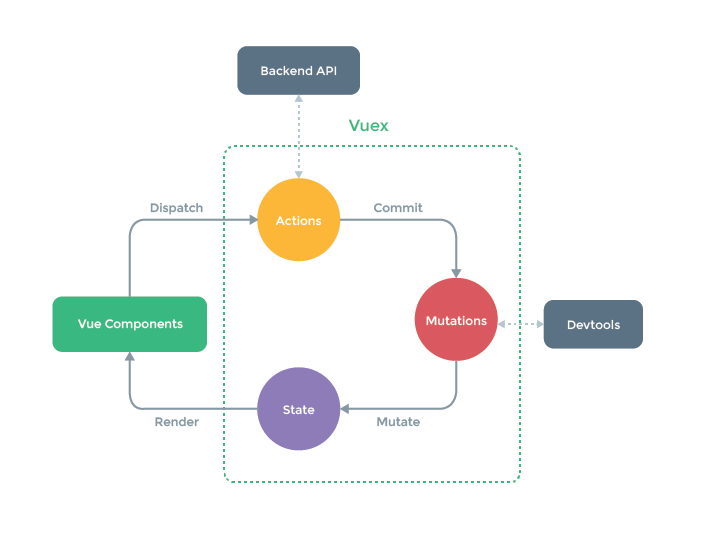
2.1 搭建VueX环境
2.1.1 创建文件
src/store/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const actions = {}
const mutations = {}
const state = {}
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state
})
|
2.1.2 传入store配置项
在main.js中创建vm时传入store配置项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| ...
import store from './store'
...
new Vue({
el:'#app',
render: h => h(App),
store
})
|
2.2 VueX案例——基本使用
Count.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{{$store.state.sum}}</h1>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Count',
data() {
return {
n:1,
}
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n)
},
decrement(){
this.$store.commit('JIAN',this.n)
},
incrementOdd(){
this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd',this.n)
},
incrementWait(){
this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait',this.n)
},
},
mounted() {
console.log('Count',this)
},
}
</script>
<style lang="css">
button{
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
|
/src/store/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const actions = {
jiaOdd(context,value){
console.log('actions中的jiaOdd被调用了')
if(context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit('JIA',value)
}
},
jiaWait(context,value){
console.log('actions中的jiaWait被调用了')
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('JIA',value)
},500)
}
}
const mutations = {
JIA(state,value){
console.log('mutations中的JIA被调用了')
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state,value){
console.log('mutations中的JIAN被调用了')
state.sum -= value
}
}
const state = {
sum:0
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
})
|
2.3 getters的使用
当state中的数据需要经过加工后再使用时,可以使用getters加工,有点类似计算属性
src/store/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| ...
const getters = {
bigSum(state){
return state.sum * 10
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
...
getters
})
|
读取bigSum:$store.getters.bigSum
2.4 四个map方法的使用
1
| import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
|
2.4.1 mapState
用于帮助我们映射state中的数据为计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| computed: {
...mapState({sum:'sum',school:'school',subject:'subject'}),
...mapState(['sum','school','subject']),
},
|
2.4.2 mapGetters
用于帮助我们映射getters中的数据为计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| computed: {
...mapGetters({bigSum:'bigSum'}),
...mapGetters(['bigSum'])
},
|
2.4.3 mapActions
用于帮助我们生成与actions对话的方法,即:包含$store.dispatch(xxx)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| methods:{
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'})
...mapActions(['jiaOdd','jiaWait'])
}
|
2.4.4 mapMutations
用于帮助我们生成与mutations对话的方法,即:包含$store.commit(xxx)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| methods:{
...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
...mapMutations(['JIA','JIAN']),
}
|
2.4.5 案例完善
mapActions与mapMutationsz在使用时,若要传递参数,需在模板中绑定事件时传递好参数,否则参数是事件对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| <template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h1>
<h3>当前求和放大10倍为:{{bigSum}}</h3>
<h3>我在{{school}},学习{{subject}}</h3>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+</button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'Count',
data() {
return {
n:1,
}
},
computed:{
...mapState(['sum','school','subject']),
...mapGetters(['bigSum'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'})
},
}
</script>
<style lang="css">
button{
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
|
2.5 store模块化
让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确
2.5.1 修改store.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| const countAbout = {
namespaced:true,
state:{ ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const personAbout = {
namespaced:true,
state:{ ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countAbout,
personAbout
}
})
|
2.5.2 读取state数据
1
2
3
4
5
|
this.$store.state.personAbout.xxx
...mapState('countAbout',['sum','school','subject'])
|
2.5.3 读取getters数据
1
2
3
4
5
|
this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName']
...mapGetters('countAbout',['bigSum'])
|
2.5.4 组件中调用dispatch
1
2
3
4
5
|
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang',person)
...mapActions('countAbout',{incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'})
|
2.5.5 组件中调用commit
1
2
3
4
5
|
this.$store.commit('personAbout/ADD_PERSON',person)
...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
|
三、Vue-Router
- 理解: 一个路由(route)就是一组映射关系(key -
value),多个路由需要路由器(router)进行管理
- 前端路由:key是路径,value是组件
3.1 基本使用
- 路由组件通常存放在
pages文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹
- 通过切换,“隐藏”了的路由组件,默认是被销毁掉的,需要的时候再去挂载
- 每个组件都有自己的
$route属性,里面存储着自己的路由信息
- 整个应用只有一个router,可以通过组件的
$router属性获取到
3.1.1 创建文件
src/router/index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import About from '../components/About'
import Home from '../components/Home'
export default new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
path:'/about',
component:About
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home
}
]
})
|
3.1.2 注册路由
main.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(VueRouter)
new Vue({
el:'#app',
render: h => h(App),
router:router
})
|
3.1.3 router-link实现切换
1
2
|
<router-link active-class="active" to="/about">About</router-link>
|
3.1.4 router-view指定展示位置
1
| <router-view></router-view>
|
3.2 多级路由
3.2.1 children配置项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| export default new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
path:'/about',
component:About
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
children: [
{
path:'news',
component: New
}
]
}
]
})
|
3.2.2 路由跳转
1
2
|
<router-link to="/home/news">News</router-link>
|
3.3 命名路由
可以简化路由的跳转
3.3.1 给路由命名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| export default new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
children: [
{
path: 'message',
component: Message,
children: [
{
path:'detail',
name:'xiangqing',
component:Detail,
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
|
3.3.2 简化跳转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<router-link to="/home/message/detail">跳转</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'xiangqing'}">跳转</router-link>
<router-link
:to="{
name:'hello',
}"
>跳转</router-link>
|
3.4 query参数
3.4.1 传递参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<router-link :to="/home/message/detail?id=666&title=你好">跳转</router-link>
<router-link
:to="{
path:'/home/message/detail',
query:{
id:666,
title:'你好'
}
}"
>跳转</router-link>
|
3.4.2 接收参数
1
2
| $route.query.id
$route.query.title
|
3.5 params参数
3.5.1 传递参数
路由携带params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,则不能使用path配置项,必须使用name配置!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<router-link :to="/home/message/detail/666/你好">跳转</router-link>
<router-link
:to="{
name:'xiangqing',
params:{
id:666,
title:'你好'
}
}"
>跳转</router-link>
|
3.5.2 声明接收params参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| export default new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
children: [
{
component: Message,
children: [
{
name:'xiangqing',
path:'detail/:id/:title',
component:Detail,
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
|
3.5.3 接收参数
1
2
| $route.params.id
$route.params.title
|
3.6 路由的props配置
让路由组件更方便的收到参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| {
name:'xiangqing',
path:'detail/:id',
component:Detail,
props:{a:900}
props(route){
return {
id: route.query.id,
title: route.query.title
}
}
props:true
}
|
3.7
<router-link>的replace属性
- 作用:控制路由跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式
- 浏览器的历史记录有两种写入方式:分别为
push和replace,push是追加历史记录,replace是替换当前记录(一个类似于栈的结构)。路由跳转时候默认为push
开启replace模式:
1
| <router-link replace>News</router-link>
|
3.8 编程式路由导航
不借助<router-link>实现路由跳转,让路由跳转更加灵活
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
this.$router.push({
name:'xiangqing',
params:{
id:xxx,
title:xxx
}
})
this.$router.replace({
name:'xiangqing',
params:{
id:xxx,
title:xxx
}
})
this.$router.forward()
this.$router.back()
this.$router.go()
|
3.9 缓存路由组件
让不展示的路由组件保持挂载,不被销毁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<keep-alive include="News">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
<keep-alive :include="['News','Message']">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
|
3.10 两个新的生命周期钩子
- 路由组件所独有的两个钩子,用于捕获路由组件的激活状态
- 具体名字
activated路由组件被激活时触发deactivated路由组件失活时触发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <script>
export default {
name:'News',
activated() {
console.log('News组件被激活了')
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
this.opacity -= 0.01
if(this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1
},16)
},
deactivated() {
console.log('News组件失活了')
clearInterval(this.timer)
},
}
</script>
|
3.11 路由守卫
对路由进行权限控制
可以在src/router/index.js配置路由的元信息meta字段:
1
| meta:{isAuth:true,title:'新闻'}
|
3.11.1 全局守卫
在src/router/index.js最后添加以下两个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
console.log('beforeEach',to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){
if(localStorage.getItem('school') === 'atguigu'){
next()
}else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}else{
next()
}
})
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log('afterEach',to,from)
if(to.meta.title){
document.title = to.meta.title
}else{
document.title = 'vue_test'
}
})
|
3.11.2 独享守卫
在src/router/index.js中对应的路由处添加beforeEnter方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| {
name:'xinwen',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'新闻'},
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log('独享路由守卫',to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){
if(localStorage.getItem('school')==='atguigu'){
next()
}else{
alert('学校名不对,无权限查看!')
}
}else{
next()
}
}
},
|
3.11.3 组件内守卫
放在组件内部使用,同钩子使用方法一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
...
},
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
...
}
|
3.12 路由器的两种工作模式
- 对于一个url来说,什么是hash值?—— #及其后面的内容就是hash值
- hash值不会包含在 HTTP 请求中,即:hash值不会带给服务器
- hash模式:
- 地址中永远带着#号,不美观
- 若以后将地址通过第三方手机app分享,若app校验严格,则地址会被标记为不合法
- 兼容性较好
- history模式:
- 地址干净,美观
- 兼容性和hash模式相比略差
- 应用部署上线时需要后端人员支持,解决刷新页面服务端404的问题
四、Vue UI组件库
4.1 移动端常用UI组件库
Vant:https://youzan.gothub.io/vantCube UI: https://didi.github.io/cube-uiMint UI: https//mint-ui.github.io
4.2 PC端常用UI组件库
Element UI: https://element.eleme.cnIView UI: https://www.iviewui.com
4.3 Element UI
4.3.1 安装
4.3.2 完整引入
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import Vue from 'vue';
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
import App from './App.vue';
Vue.use(ElementUI);
|
4.3.3 按需引入
首先,安装babel-plugin-component:
1
| npm install babel-plugin-component -D
|
接着,修改babel.config.js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| module.exports = {
presets: [
'@vue/cli-plugin-babel/preset',
["@babel/preset-env", { "modules": false }],
],
plugins:[
[
"component",
{
"libraryName": "element-ui",
"styleLibraryName": "theme-chalk"
}
]
]
}
|
最后,main.js按需引入:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import Vue from 'vue';
import { Button, Select } from 'element-ui';
import App from './App.vue';
Vue.component(Button.name, Button);
Vue.component(Select.name, Select);
|
